Mobile App Development, SEO, Social Media, Web Development
9 Common Technical SEO Issues That Actually Matter
- By Brett Belau
31 Jan

In this article, we’ll see how to find and fix technical SEO issues, but only those that can seriously affect your rankings.
If you’d like to follow along, get Ahrefs Webmaster Tools and Google Search Console (both are free) and check for the following issues.
Indexability is a webpage’s ability to be indexed by search engines. Pages that are not indexable can’t be displayed on the search engine results pages and can’t bring in any search traffic.
Three requirements must be met for a page to be indexable:
- The page must be crawlable. If you haven’t blocked Googlebot from entering the page robots.txt or you have a website with fewer than 1,000 pages, you probably don’t have an issue there.
- The page must not have a noindex tag (more on that in a bit).
- The page must be canonical (i.e., the main version).
Solution
In Ahrefs Webmaster Tools (AWT):
- Open Site Audit
- Go to the Indexability report
- Click on issues related to canonicalization and “noindex” to see affected pages
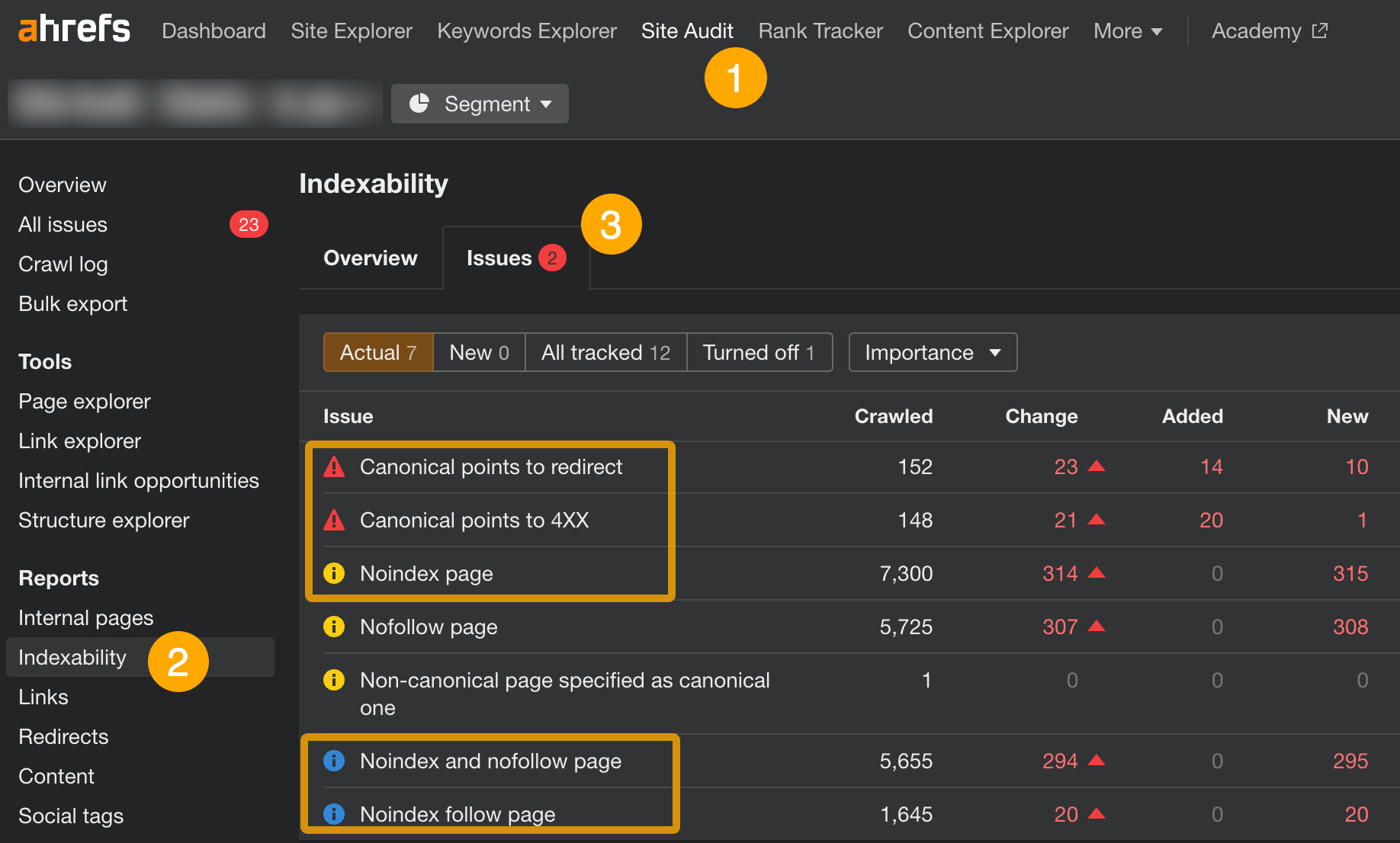
For canonicalization issues in this report, you will need to replace bad URLs in the link rel="canonical" tag with valid ones (i.e., returning an “HTTP 200 OK”).
As for pages marked by “noindex” issues, these are the pages with the “noindex” meta tag placed inside their code. Chances are most of the pages found in the report there should stay as is. But if you see any pages that shouldn’t be there, simply remove the tag. Do make sure those pages aren’t blocked by robots.txt first.
Recommendation
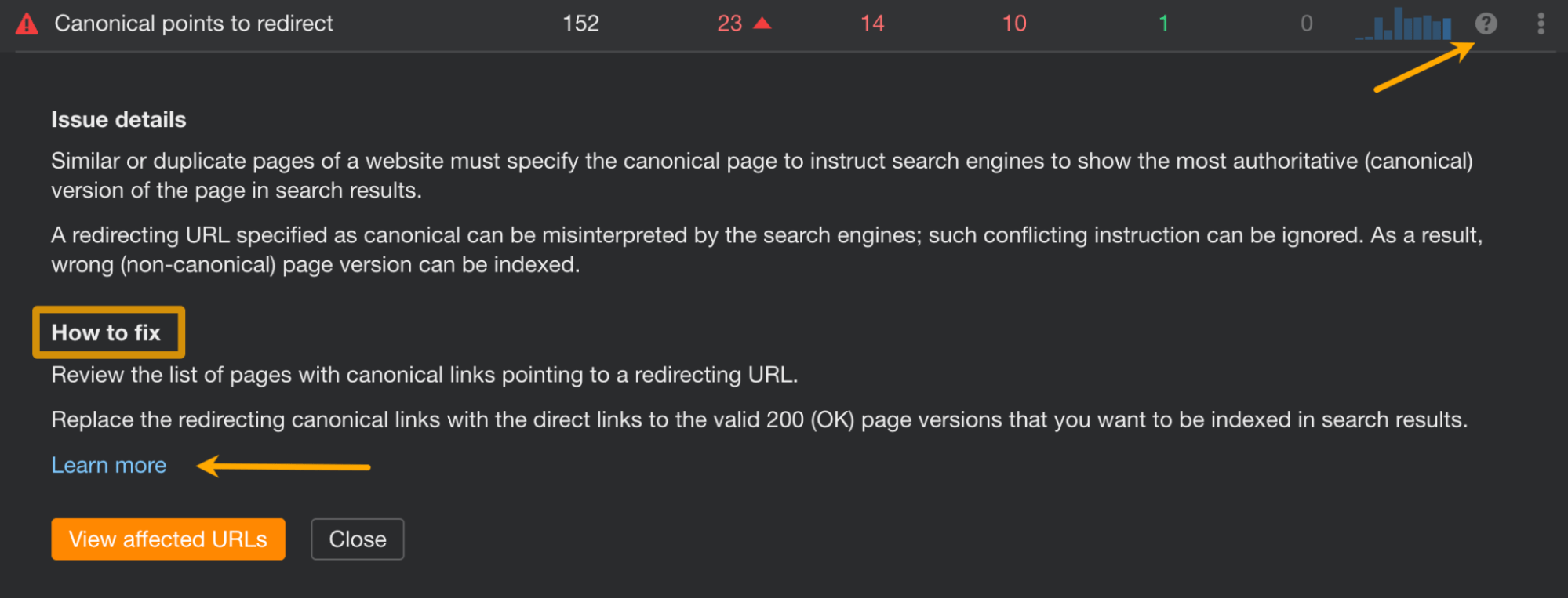
A sitemap should contain only pages that you want search engines to index.
When a sitemap isn’t regularly updated or an unreliable generator has been used to make it, a sitemap may start to show broken pages, pages that became “noindexed,” pages that were de-canonicalized, or pages blocked in robots.txt.
Solution
In AWT:
- Open Site Audit
- Go to the All issues report
- Click on issues containing the word “sitemap” to find affected pages
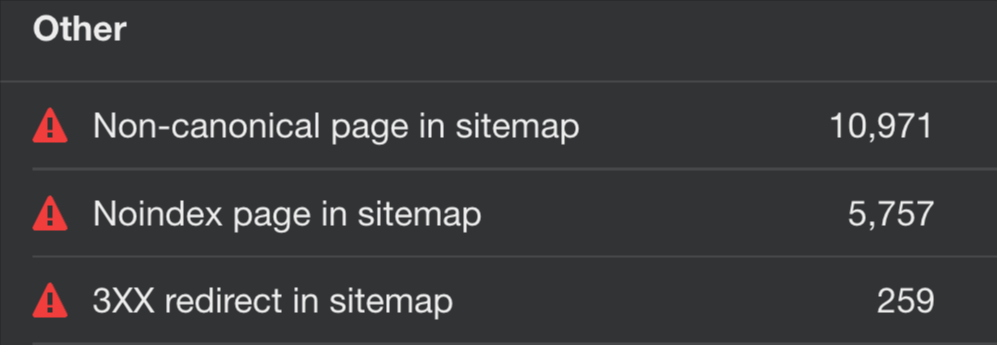
Depending on the issue, you will have to:
- Delete the pages from the sitemap.
- Remove the noindex tag on the pages (if you want to keep them in the sitemap).
- Provide a valid URL for the reported page.
Google uses HTTPS encryption as a small ranking signal. This means you can experience lower rankings if you don’t have an SSL or TLS certificate securing your website.
But even if you do, some pages and/or resources on your pages may still use the HTTP protocol.
Solution
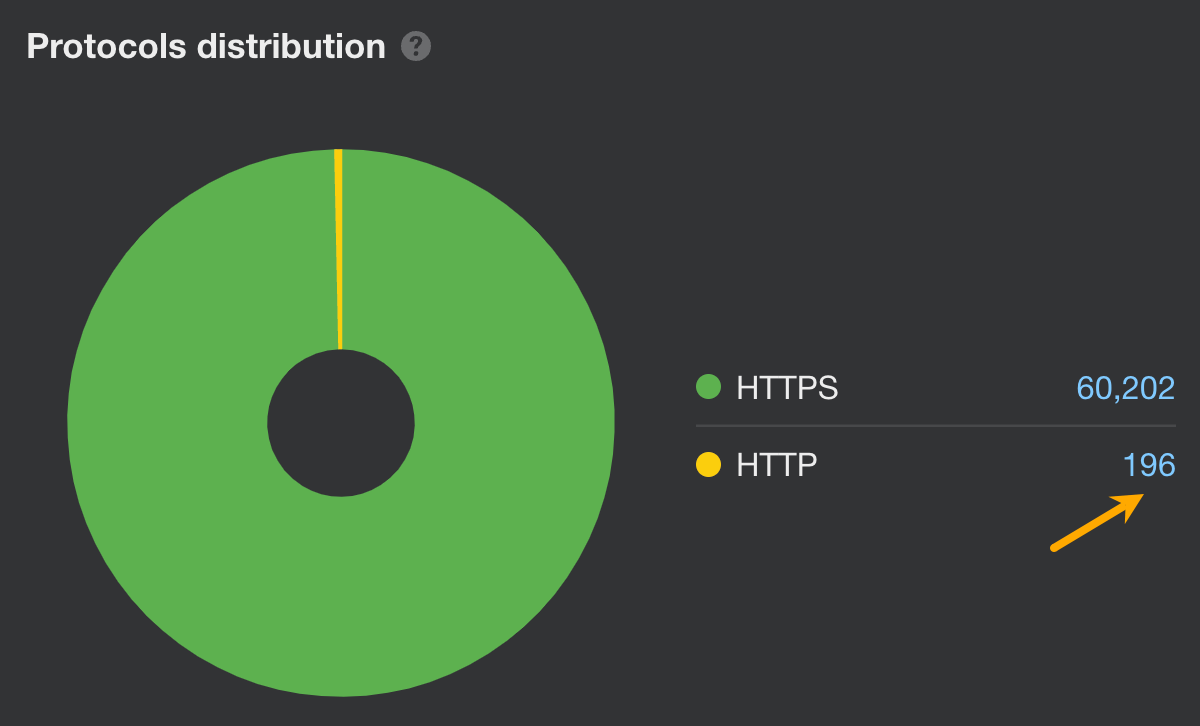
Assuming you already have an SSL/TLS certificate for all subdomains (if not, do get one), open AWT and do these:
- Open Site Audit
- Go to the Internal pages report
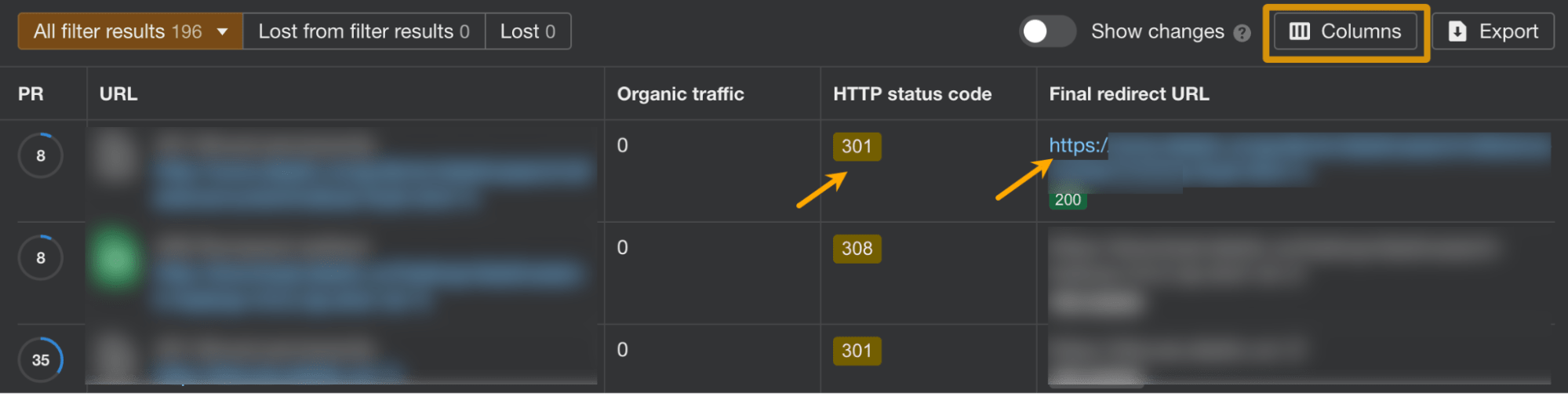
- Look at the protocol distribution graph and click on HTTP to see affected pages
- Inside the report showing pages, add a column for Final redirect URL
- Make sure all HTTP pages are permanently redirected (301 or 308 redirects) to their HTTPS counterparts
Finally, let’s check if any resources on the site still use HTTP:
- Inside the Internal pages report, click on Issues
- Click on HTTPS/HTTP mixed content to view affected resources
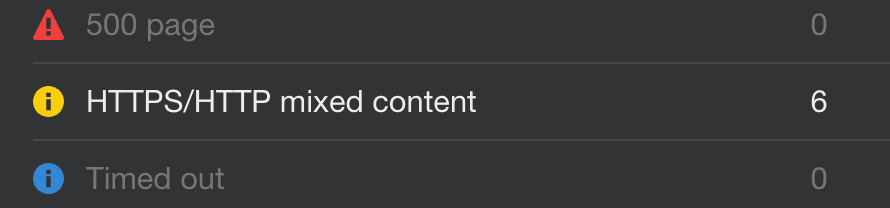
You can fix this issue by one of these methods:
- Link to the HTTPS version of the resource (check this option first)
- Include the resource from a different host, if available
- Download and host the content on your site directly if you are legally allowed to do so
- Exclude the resource from your site altogether
Learn more: What Is HTTPS? Everything You Need to Know
Duplicate content happens when exact or near-duplicate content appears on the web in more than one place.
It’s bad for SEO mainly for two reasons: It can cause undesirable URLs to show in search results and can dilute link equity.
Content duplication is not necessarily a case of intentional or unintentional creation of similar pages. There are other less obvious causes such as faceted navigation, tracking parameters in URLs, or using trailing and non-trailing slashes.
Solution
First, check if your website is available under only one URL. Because if your site is accessible as:
- http://domain.com
- http://www.domain.com
- https://domain.com
- https://www.domain.com
Then Google will see all of those URLs as different websites.
The easiest way to check if users can browse only one version of your website: type in all four variations in the browser, one by one, hit enter, and see if they get redirected to the master version (ideally, the one with HTTPS).
You can also go straight into Site Audit’s Duplicates report. If you see 100% bad duplicates, that is likely the reason.
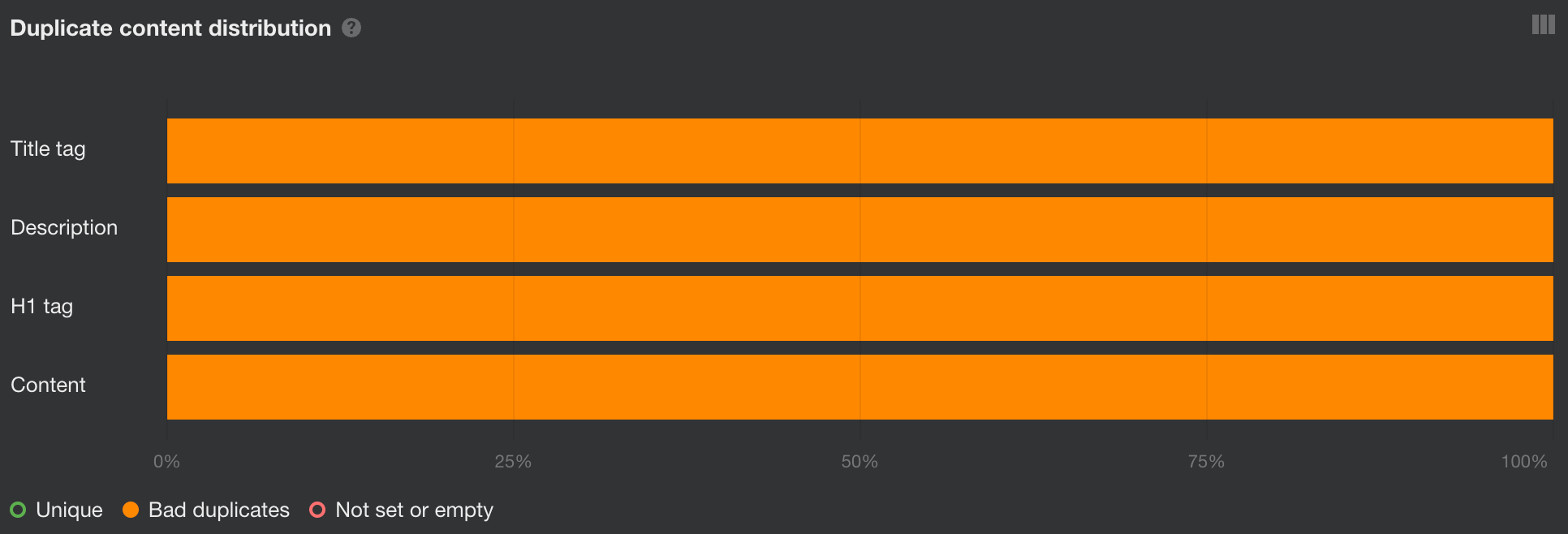
In this case, choose one version that will serve as canonical (likely the one with HTTPS) and permanently redirect other versions to it.
Then run a New crawl in Site Audit to see if there are any other bad duplicates left.
There are a few ways you can handle bad duplicates depending on the case. Learn how to solve them in our guide.
Learn more: Duplicate Content: Why It Happens and How to Fix It
Pages that can’t be found (4XX errors) and pages returning server errors (5XX errors) won’t be indexed by Google so they won’t bring you any traffic.
Furthermore, if broken pages have backlinks pointing to them, all of that link equity goes to waste.
Broken pages are also a waste of crawl budget—something to watch out for on bigger websites.
Solution
In AWT, you should:
- Open Site Audit.
- Go to the Internal pages report.
- See if there are any broken pages. If so, the Broken section will show a number higher than 0. Click on the number to show affected pages.
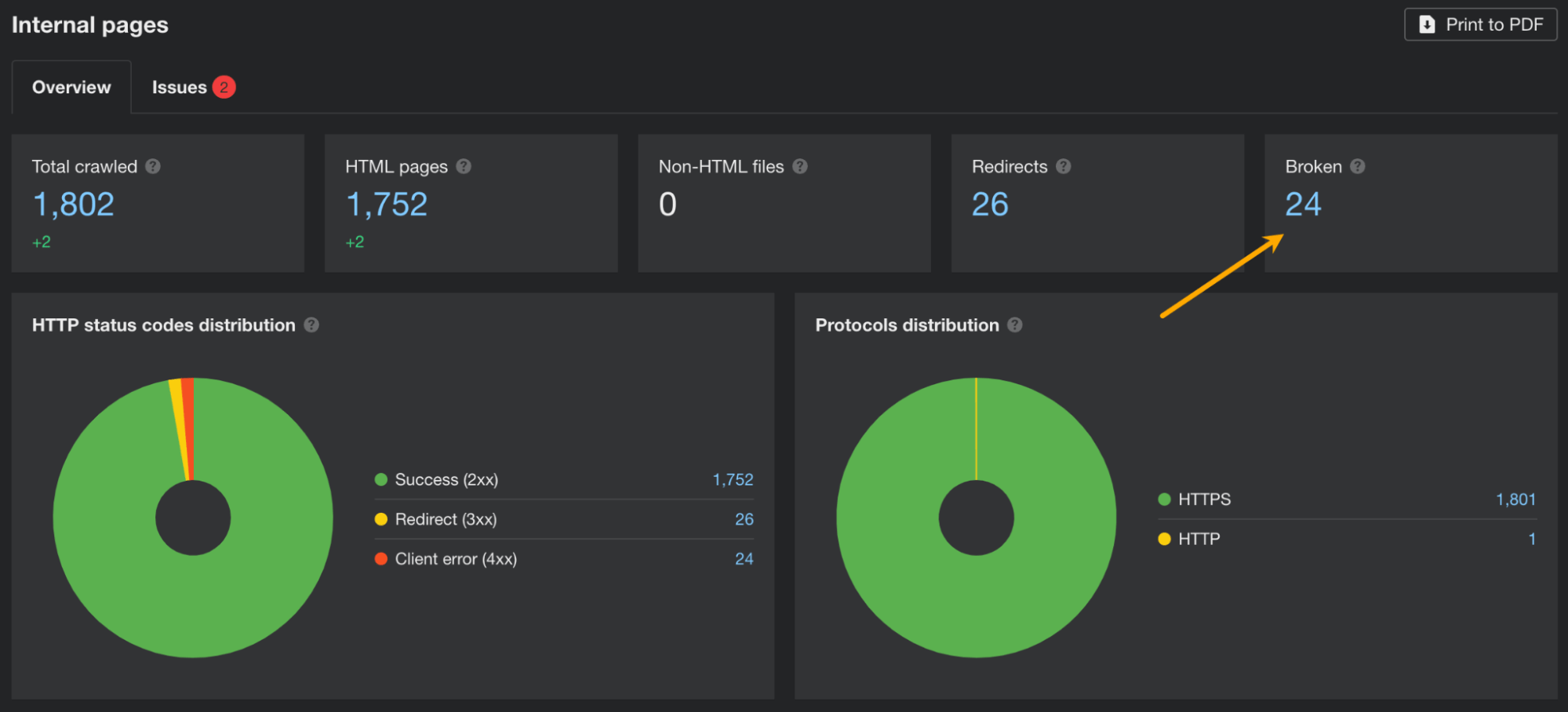
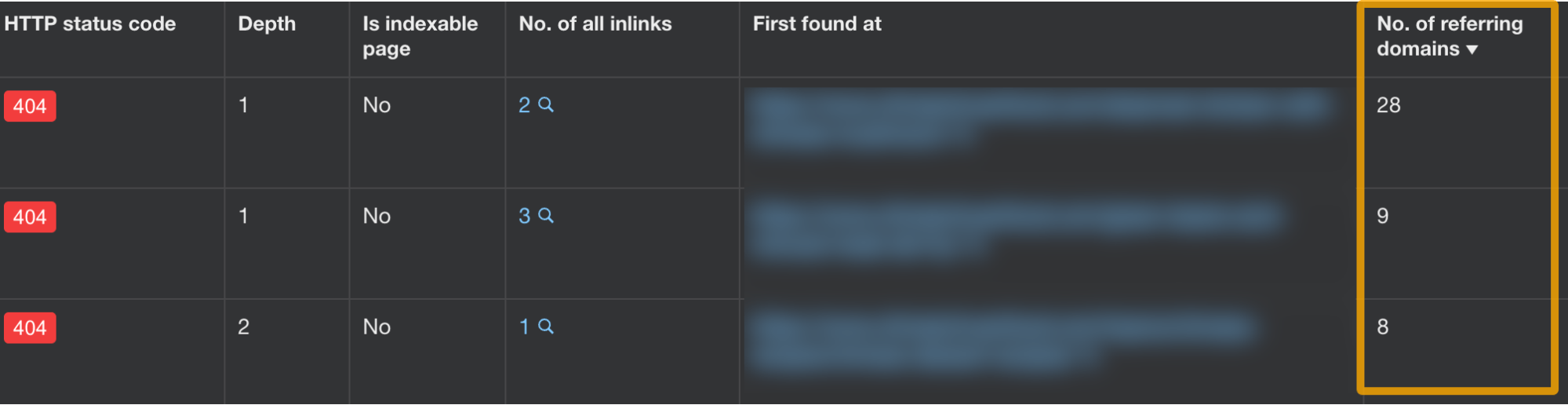
In the report showing pages with issues, it’s a good idea to add a column for the number of referring domains. This will help you make the decision on how to fix the issue.
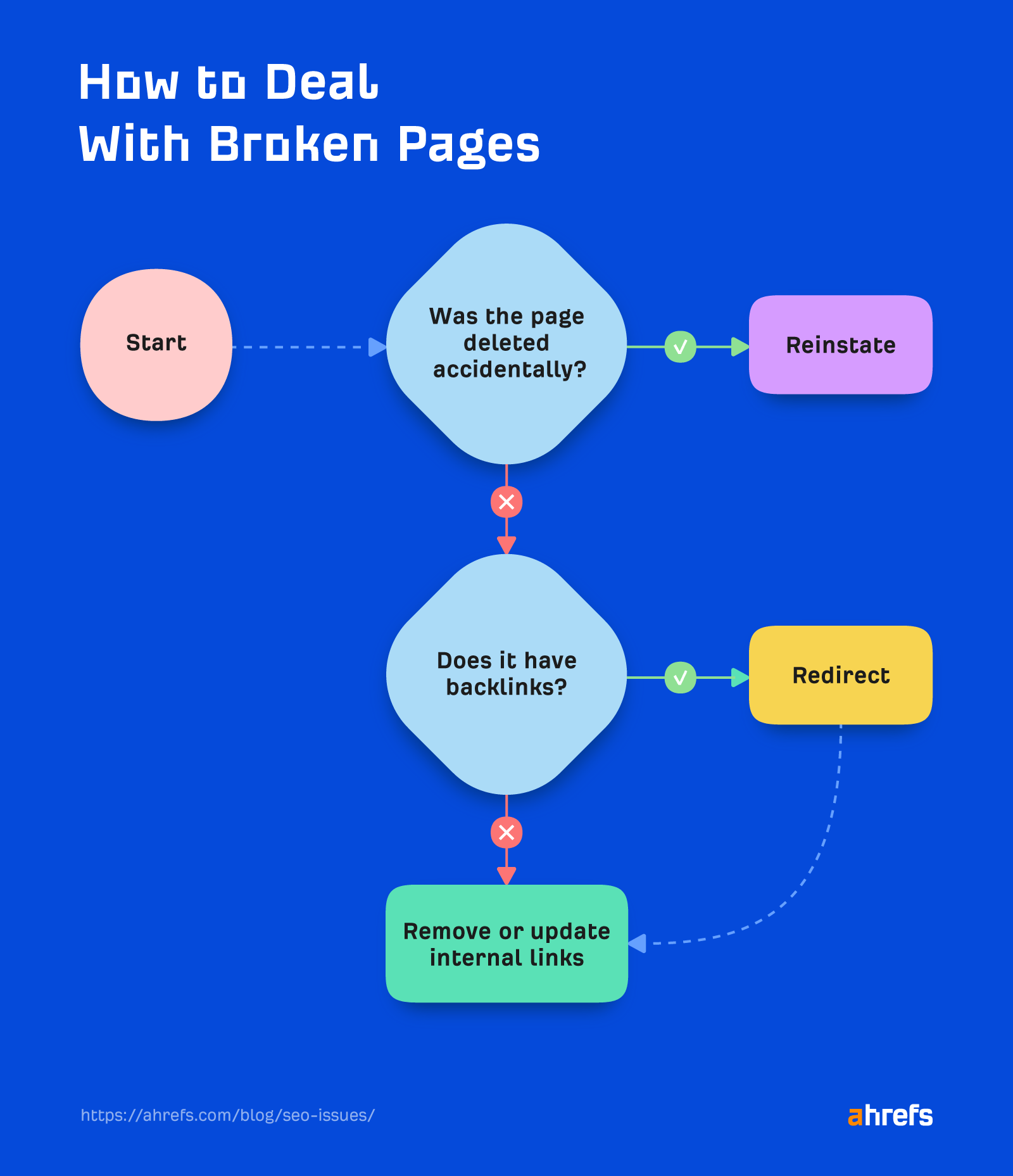
Now, fixing broken pages (4XX error codes) is quite simple, but there is more than one possibility. Here’s a short graph explaining the process:
Dealing with server errors (the ones reporting a 5XX) can be a tougher one, as there are different possible reasons for a server to be unresponsive. Read this short guide for troubleshooting.
Recommendation
- Go to Site Explorer
- Enter your domain
- Go to the Best by links report
- Add a “404 not found” filter
- Then sort the report by referring domains from high to low
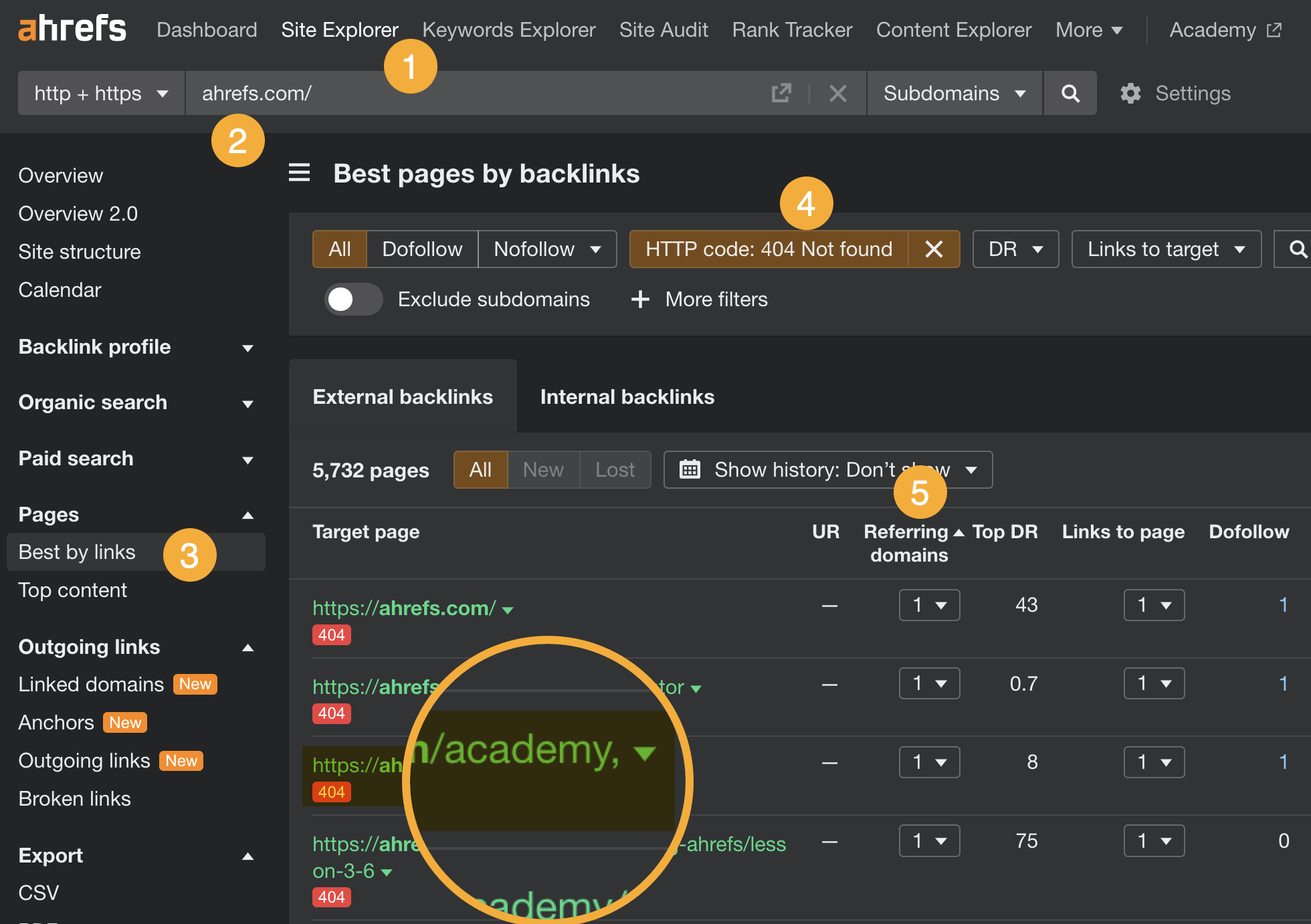
If you’ve already dealt with broken pages, chances are you’ve fixed most of the broken links issues.
Other critical issues related to links are:
- Orphan pages – These are the pages without any internal links. Web crawlers have limited ability to access those pages (only from sitemap or backlinks), and there is no link equity flowing to them from other pages on your site. Last but not least, users won’t be able to access this page from the site navigation.
- HTTPS pages linking to internal HTTP pages – If an internal link on your website brings users to an HTTP URL, web browsers will likely show a warning about a non-secure page. This can damage your overall website authority and user experience.
Solution
In AWT, you can:
- Go to Site Audit.
- Open the Links report.
- Open the Issues tab.
- Look for the following issues in the Indexable category. Click to see affected pages.
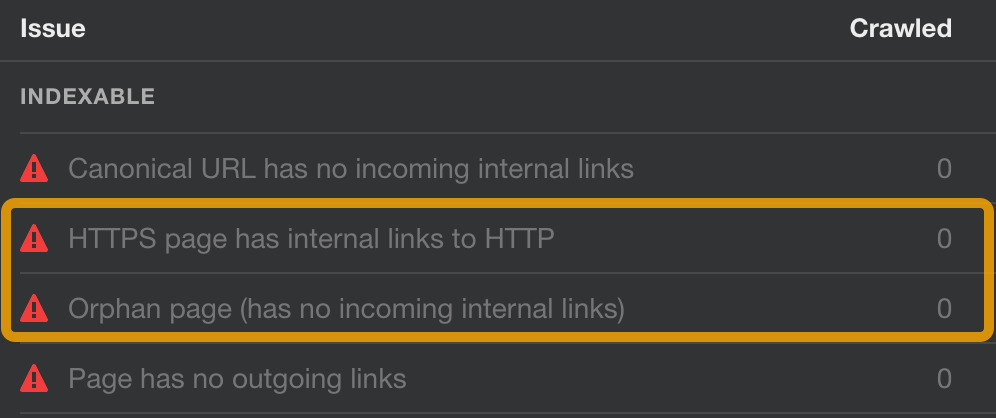
Fix the first issue by changing the links from HTTP to HTTPS or simply delete those links if no longer needed.
For the second issue, an orphan page needs to be either linked to from some other page on your website or deleted if a given page holds no value to you.
Sidenote.
Ahrefs’ Site Audit can find orphan pages as long as they have backlinks or are included in the sitemap. For a more thorough search for this issue, you will need to analyze server logs to find orphan pages with hits. Find out how in this guide.
Having a mobile-friendly website is a must for SEO. Two reasons:
- Google uses mobile-first indexing – It’s mostly using the content of mobile pages for indexing and ranking.
- Mobile experience is part of the Page Experience signals – While Google will allegedly always “promote” the page with the best content, page experience can be a tiebreaker for pages offering content of similar quality.
Solution
In GSC:
- Go to the Mobile Usability report in the Experience section
- View affected pages by clicking on issues in the Why pages aren’t usable on mobile section
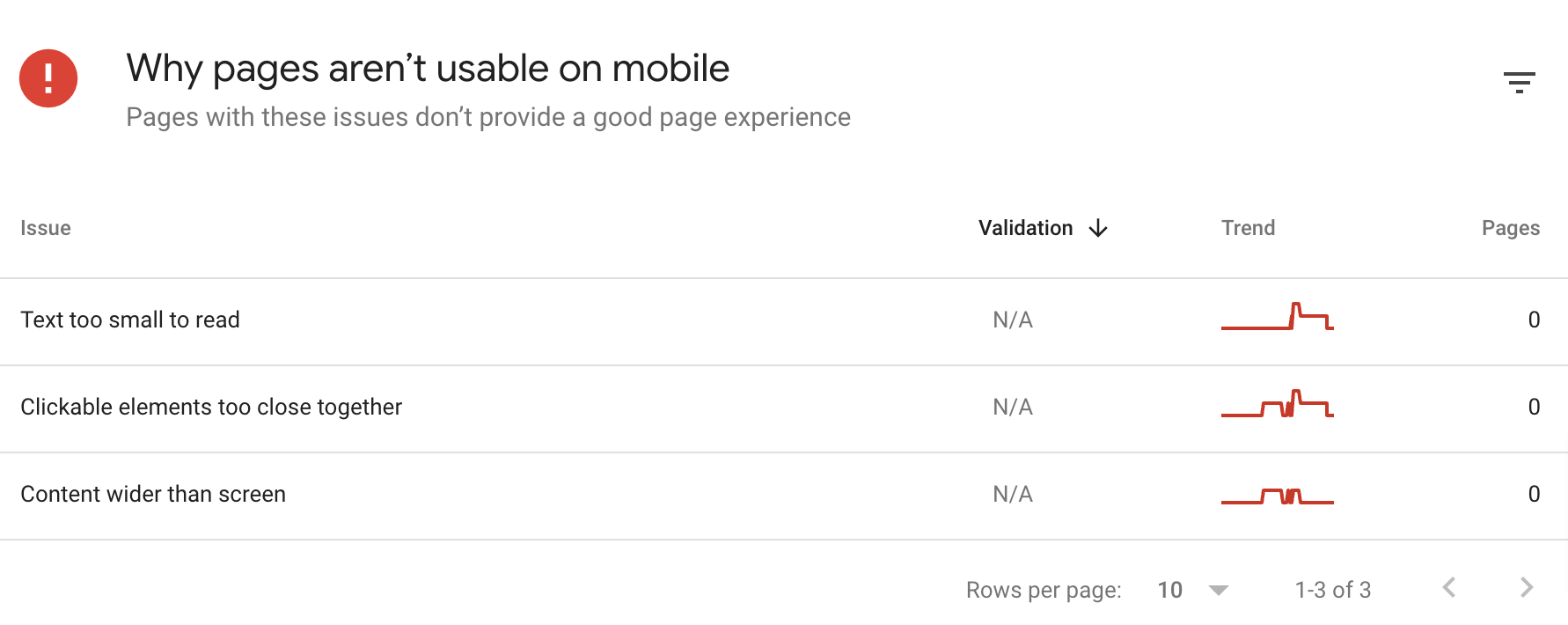
You can read Google’s guide for fixing mobile issues here.
Performance and visual stability are other aspects of Page Experience signals used by Google to rank pages.
Google has developed a special set of metrics to measure user experience called Core Web Vitals (CWV). Site owners and SEOs can use those metrics to see how Google perceives their website in terms of UX.
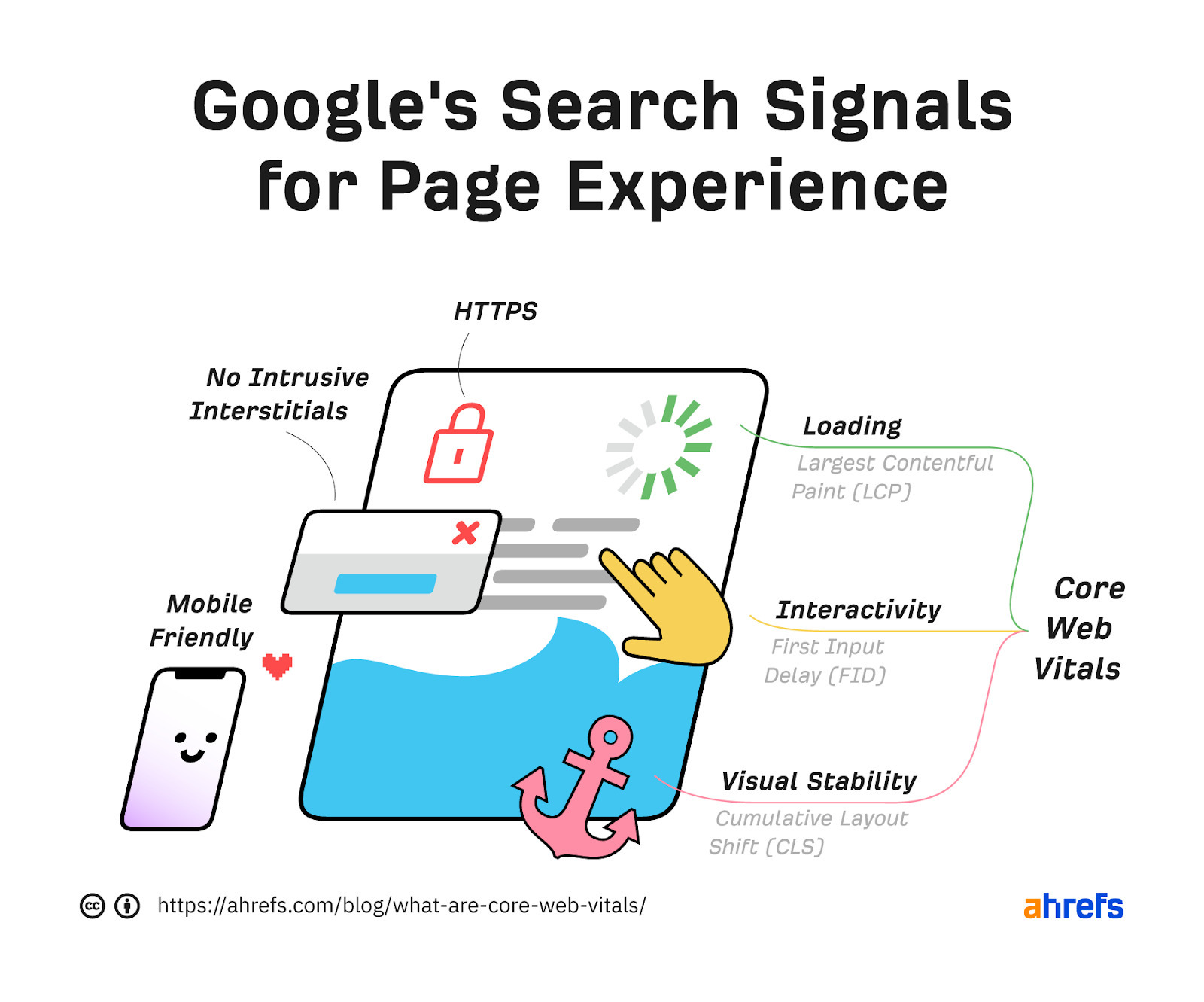
While page experience can be a ranking tiebreaker, CWV is not a race. You don’t need to have the fastest website on the internet. You just need to score “good” ideally in all three categories: loading, interactivity, and visual stability.
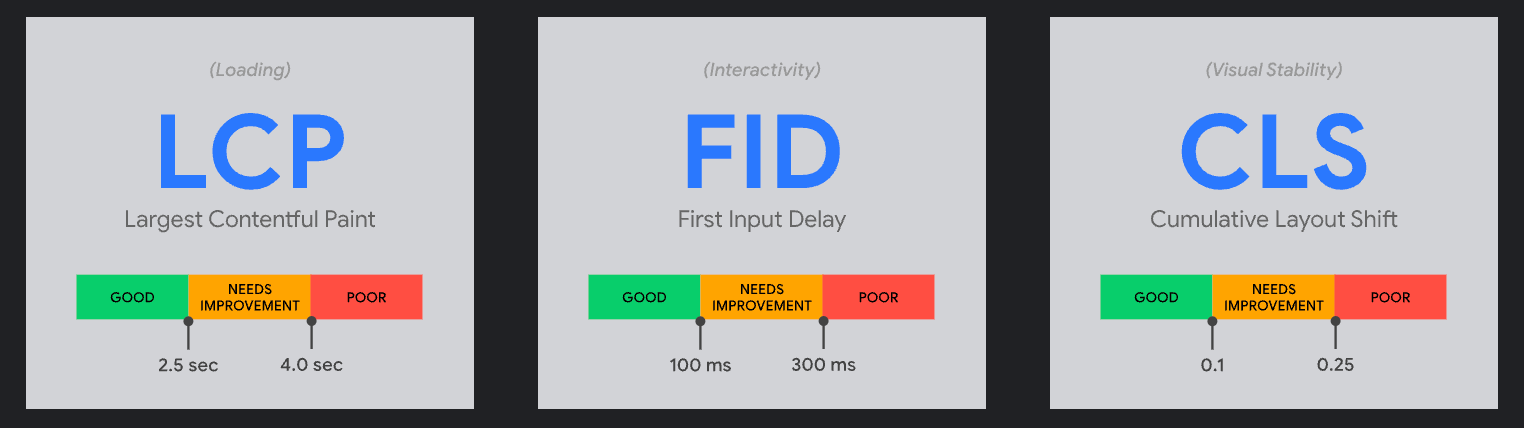
Solution
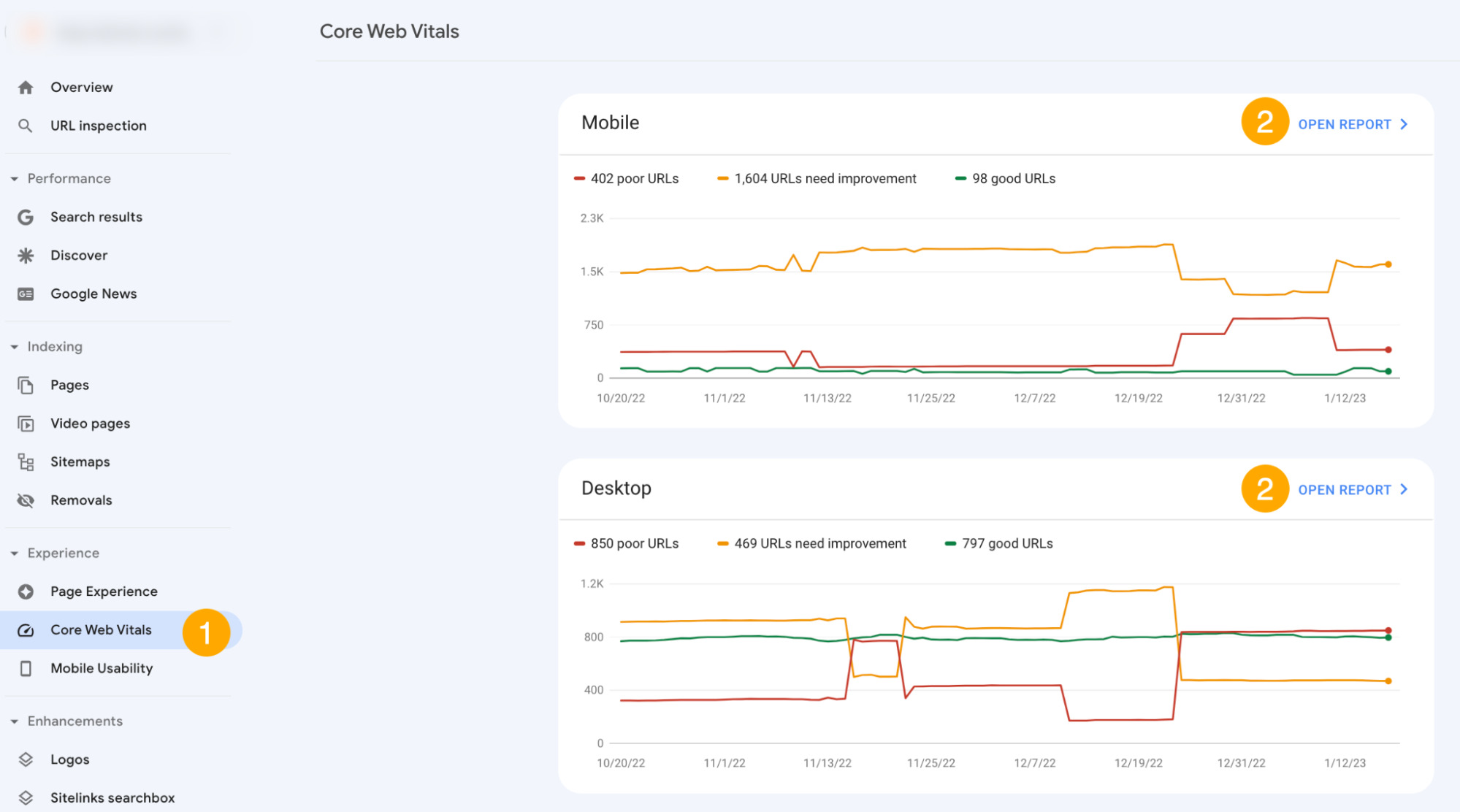
In GSC:
- First, click on Core Web Vitals in the Experience section of the reports.
- Then click Open report in each section to see how your website scores.
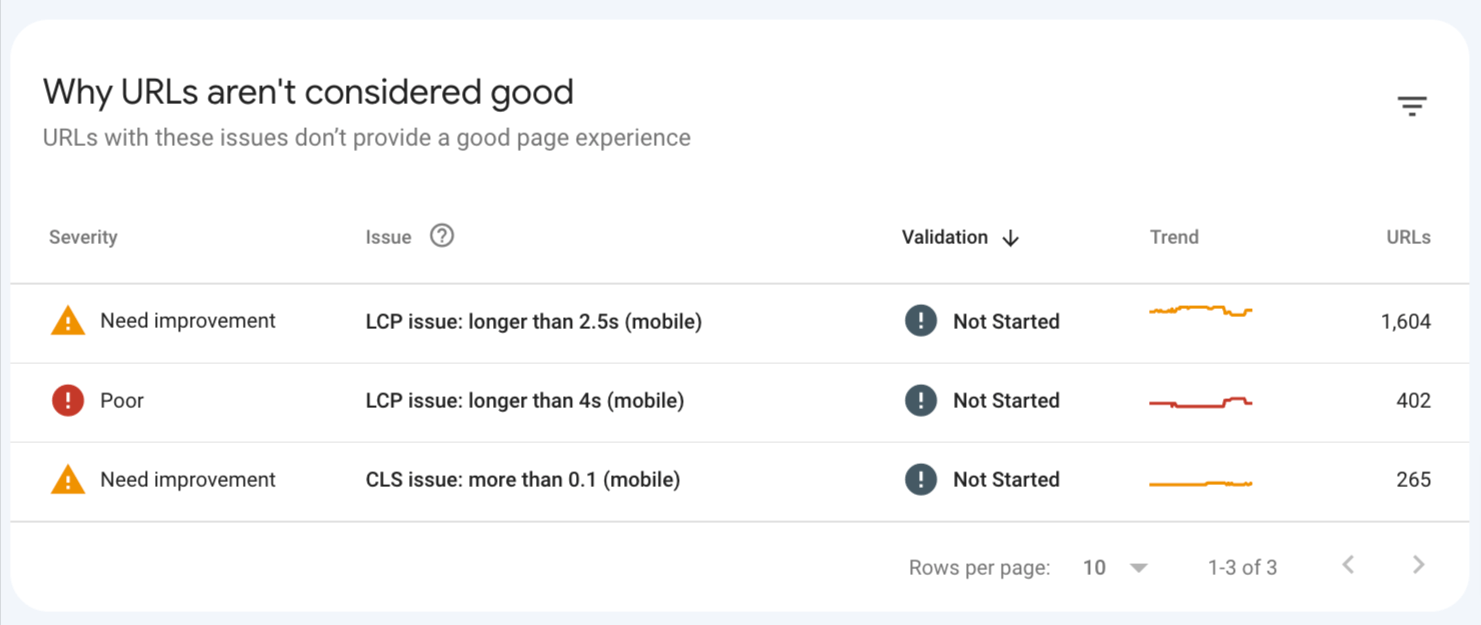
- For pages that aren’t considered good, you’ll see a special section at the bottom of the report. Use it to see pages that need your attention.
Optimizing for CWV may take some time. This may include things like moving to a faster (or closer) server, compressing images, optimizing CSS, etc. We explain how to do this in the third part of this guide to CWV.
Bad website structure in the context of technical SEO is mainly about having important organic pages too deep into the website structure.
Pages that are nested too deep (i.e., users need >6 clicks from the website to get to them) will receive less link equity from your homepage (likely the page with the most backlinks), which may affect their rankings. This is because link value diminishes with every link “hop.”
Sidenote.
Website structure is important for other reasons too such as the overall user experience, crawl efficiency, and helping Google understand the context of your pages. Here, we’ll only focus on the technical aspect, but you can read more about the topic in our full guide: Website Structure: How to Build Your SEO Foundation.
Solution
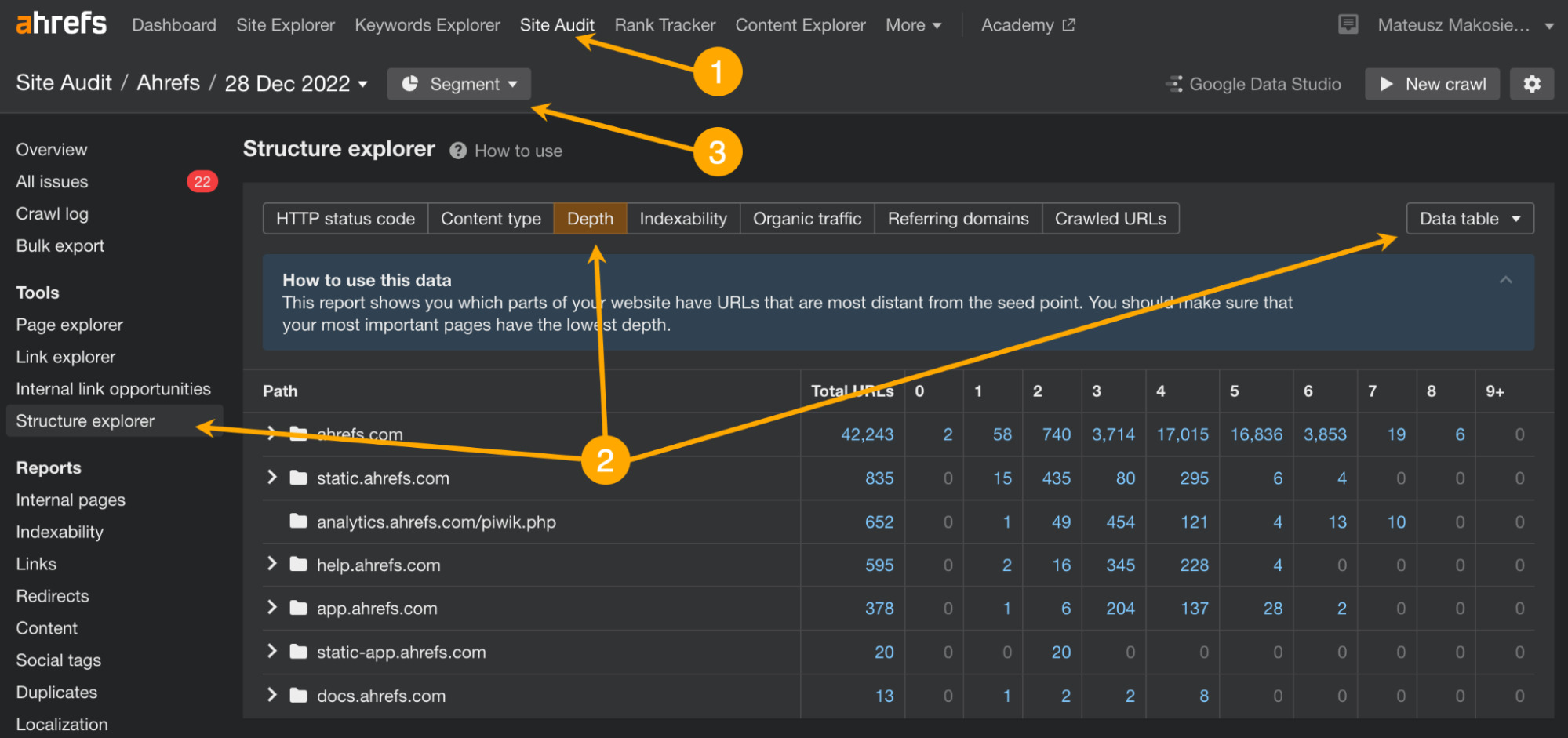
In AWT:
- Open Site Audit
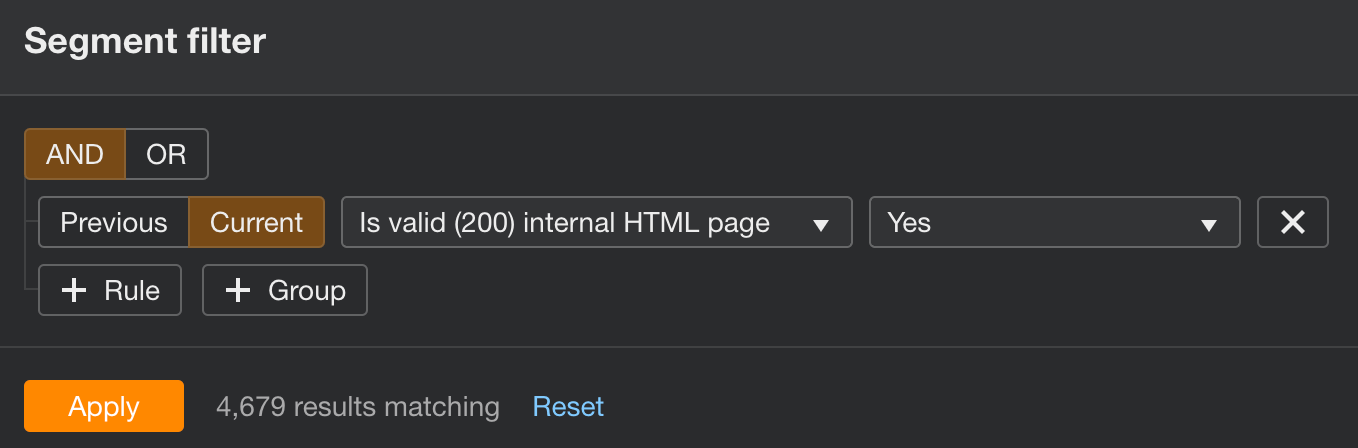
- Go to Structure explorer, switch to the Depth tab, and set the data type to Data table
- Configure the Segment to only valid HTML pages and click Apply
- Use the graph to investigate pages with more than six clicks away from the homepage
The way to fix the issue is to link to these deeper nested pages from pages closer to the homepage. More important pages could find their place in site navigation, while less important ones can be just linked to the pages a few clicks closer.
It’s a good idea to weigh in user experience and the business role of your website when deciding what goes into sitewide navigation.
For example, we could probably give our SEO glossary a slightly higher chance to get ahead of organic competitors by including it in the main site navigation. Yet we decided not to because it isn’t such an important page for users who are not particularly searching for this type of information.
We’ve moved the glossary only up a notch by including a link inside the beginner’s guide to SEO (which itself is just one click away from the homepage).
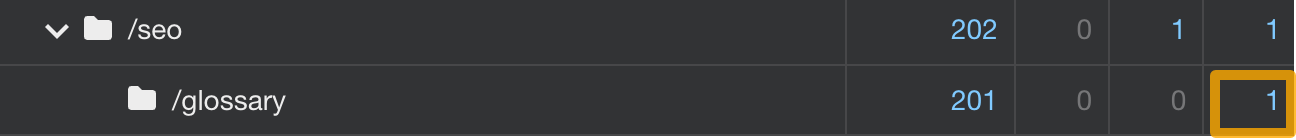

Final thoughts
When you’re done fixing the more pressing issues, dig a little deeper to keep your site in perfect SEO health. Open Site Audit and go to the All issues report to see other issues regarding on-page SEO, image optimization, redirects, localization, and more. In each case, you will find instructions on how to deal with the issue.
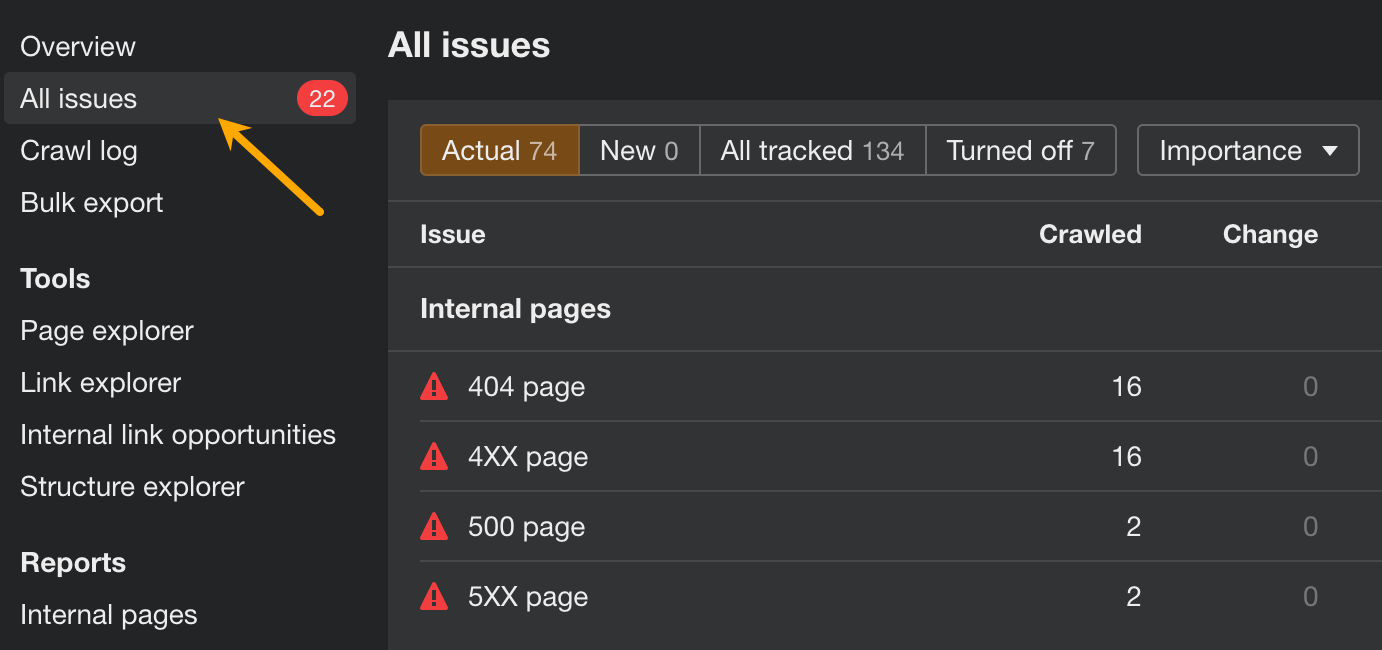
You can also customize this report by turning issues on/off or changing their priority.
Did I miss any important technical issues? Let me know on Twitter or Mastodon.
Source: ahrefs.com, originally published on 2023-01-30 23:46:34
Connect with B2 Web Studios
Get B2 news, tips and the latest trends on web, mobile and digital marketing
- Appleton/Green Bay (HQ): (920) 358-0305
- Las Vegas, NV (Satellite): (702) 659-7809
- Email Us: [email protected]

© Copyright 2002 – 2022 B2 Web Studios, a division of B2 Computing LLC. All rights reserved. All logos trademarks of their respective owners. Privacy Policy

![How to Successfully Use Social Media: A Small Business Guide for Beginners [Infographic]](https://b2webstudios.com/storage/2023/02/How-to-Successfully-Use-Social-Media-A-Small-Business-Guide-85x70.jpg)



![How to Successfully Use Social Media: A Small Business Guide for Beginners [Infographic]](https://b2webstudios.com/storage/2023/02/How-to-Successfully-Use-Social-Media-A-Small-Business-Guide-300x169.jpg)

Recent Comments